251
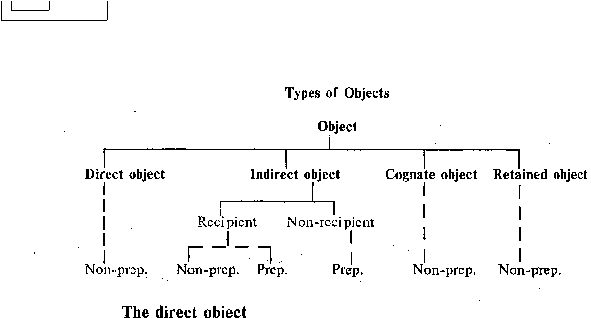
a) The indirect object of the first type is attached only to ditransitive verbs. It is expressed by a noun or
pronoun which as a rule denotes (or, in the case of pronouns, points out) a person who is the addressee or
recipient of the action of the verb. So it is convenient to call an object of this type the indirect recipient
object. It is joined to the headword either without a preposition or by the preposition to (occasionally for). The
indirect recipient object is generally used with transitive verbs.
He gave the kid two dollars.
She did not tell anything to anyone.
Will you bring a cup of coffee for me?
b) The indirect object of the second type is attached to verbs, adjectives, statives and sometimes adverbs. It
is usually a noun (less often a pronoun) denoting an inanimate object, although it may be a gerund, a gerundial
phrase or complex, an infinitive complex or a clause. Its semantics varies, but it never denotes the addressee
(recipient) of the action of the governing verb. So it may be called the indirect non-recipient object. The
indirect non-recipient object can only be joined to its headword by means of a preposition.
One must always hope for the best.
She’s not happy about her new friend.
The indirect non-recipient object is used mainly with intransitive verbs. It is usually the only object in a
sentence, at least other objects are not obligatory.
3. The cognate object is a non-prepositional object which is attached to otherwise intransitive verbs and is
always expressed by nouns derived from, or semantically related to, the root of the governing verb.
The child smiled the smile and laughed the laugh of contentment.
They struck him a heavy blow.
4. The retained object. This term is to be applied in case an active construction is transformed into a
passive one and the indirect object of the active construction becomes the subject of the passive construction.
The second object, the direct one, may be retained in the transformation, though the action of the predicate-verb
is no more directed upon it. Therefore it is called a retained object.
They gave Mary the first prize ——>
(direct object)
Mary was given the first prize
(retained object).
§ 70. The direct object is used irrespective of the absence or presence of other objects attached to the same
verb.

