18
Continuous
Is taking
Has been taking
Common
Took
Had taken
Past
Continuous
was taking
had been taking
Common
will take
will have taken
Future
Continuous
will be taking
will have been taking
Common
would take
would have taken
Future in the Past
Continuous
would be taking
would have been taking
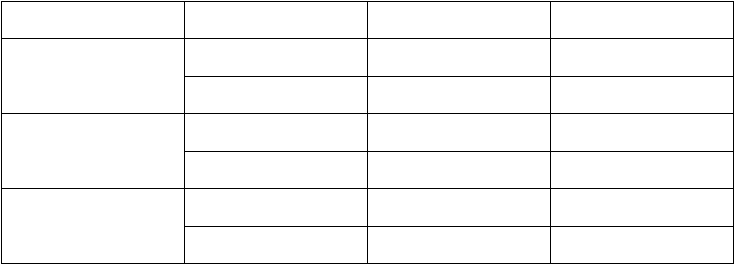
Thus each tense is represented by four verb forms involving such categories as aspect and perfect. There are
four present tense forms:
the present indefinite (the simple present)
the present continuous
the present perfect
the present perfect continuous
four past tense forms:
the past indefinite (the simple past)
the past continuous
the past perfect
the past perfect continuous
four future tense forms:
the future indefinite (the simple future)
the future continuous
the future perfect
the future perfect continuous
four future in-the-past tenses:
the future in-the-past indefinite (the simple future-in-the-past)
the future in-the-past continuous
the future in-the-past perfect
the future in-the-past perfect continuous.
Present tenses
§ 15. All the present tenses (The present indefinite, the present continuous, the present perfect, the present
perfect continuous) refer the actions they denote to the present, that is to, the time of speaking. The difference
between them lies in the way they express the categories of aspect and perfect.
The present indefinite
(The simple present)
Meaning. The present indefinite refers the action which it denotes to the present time in a broad sense.
It bears no indication as to the manner in which the action is performed, that is whether it is perfective
(complete) or imperfective (incomplete), momentary or durative (continuous), iterative or inchoative, etc. Any
of these meanings can be imparted to the form by the lexical meaning of the verb or by the context. Neither
does it bear any indication as to the precedence of the action it denotes to the moment of speaking.

