78
Here are some verbs that function in this pattern: afford, allot, bring, cause, deny, do, envy, fetch, grant,
guarantee, hand, lease, leave, lend, make, offer, owe, pass, pay, play, rent, sell, send, show, spare, tell, throw.
You will notice that certain sentences using some of the verbs listed above behave differently from the
sentences given inside the frame. All of the sentences in the frame can be rewritten with a preposition to
produce the same meaning.
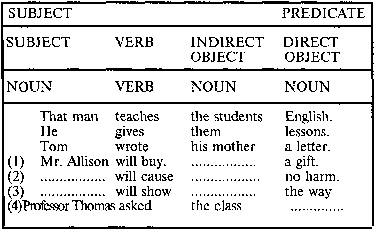
The man teaches the students English.
The man teaches English to the students.
He gives them lessons.
He gives lessons to them.
Tom wrote his mother a letter.
Tom wrote a letter to his mother.
But consider these sentences:
I envy Mary her long eyelashes.
We should spare him that humiliation.
Can you afford me a little of your time?
These sentences cannot be rewritten with prepositions. Although they have two objects they do not exactly
follow the pattern of sentences with a direct object and indirect object. Verbs that occur in sentences like these
include spare, envy, afford, cost, deny.
Can these sentences be rewritten with prepositions?
She saved him a seat.
She saved him a phone call.
The first sentence can be She saved a seat for him without a change in meaning. The second sentence,
rewritten in the same way, would lose its original meaning. In this instance, the same verb, depending on its
meaning, occurs in either variation of the pattern.
Sentence Pattern 5
This pattern appears at first to be closely related to sentence pattern 4, but on closer examination, it proves to
be quite different. In sentence pattern 4 (Noun + Verb + Noun + Noun), the two nouns that followed the verb
each referred to different things. In sentence pattern 5, also Noun + Verb + Noun + Noun, the verb is followed
by two nouns, but the two nouns refer to the same thing. The first noun after the verb is the direct object, and
the second, or last noun, is the object complement. There is an important modification of this pattern, in which
the object complement is an adjective instead of a second noun. In this case, the adjective describes the direct
object, but is also related to the action of the verb. Observe the pattern and the example sentences below.
Complete the unfinished sentences.

